| Issue |
Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys.
Volume 40, Number 2, November 2007
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 211 - 219 | |
| Section | Physics and Mechanics of Fluids, Microfluidics | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/epjap:2007151 | |
| Published online | 31 October 2007 | |
https://doi.org/10.1051/epjap:2007151
Numerical simulation of non-invasive determination of the propagation coefficient in arterial system using two measurements sites
1
Laboratoire Matière et Systèmes Complexes, CNRS UMR 7057, Université Paris VII, 2 place Jussieu, 75005 Paris, France
2
Département de Physique, Faculté des sciences de Sfax, Tunisia
3
Département de Physique, Faculté des sciences de Monastir, Tunisia
Corresponding author: patrice.flaud@paris7.jussieu.fr
Received:
30
May
2006
Revised:
28
February
2007
Accepted:
25
July
2007
Published online:
31
October
2007
Literature shows a lack of works based on non-invasive methods for computing
the propagation coefficient γ, a complex number related
to dynamic vascular properties. Its imaginary part is inversely related to
the wave speed C through the relationship 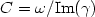 , while its real part a, called attenuation, represents loss of pulse energy per unit of length. In this
work an expression is derived giving the propagation coefficient when
assuming a pulsatile flow through a viscoelastic vessel. The effects of
physical and geometrical parameters of the tube are then studied.
In particular, the effects of increasing the reflection coefficient, on the
determination of the propagation coefficient are investigated in a first
step. In a second step, we simulate a variation of tube length under
physiological conditions. The method developed here is based on the
knowledge of instantaneous velocity and radius values at only two sites. It
takes into account the presence of a reflection site of unknown reflection
coefficient, localised in the distal end of the vessel.
The values of wave speed and attenuation obtained with this method are in a
good agreement with the theory. This method has the advantage to be usable
for small portions of the arterial tree.
, while its real part a, called attenuation, represents loss of pulse energy per unit of length. In this
work an expression is derived giving the propagation coefficient when
assuming a pulsatile flow through a viscoelastic vessel. The effects of
physical and geometrical parameters of the tube are then studied.
In particular, the effects of increasing the reflection coefficient, on the
determination of the propagation coefficient are investigated in a first
step. In a second step, we simulate a variation of tube length under
physiological conditions. The method developed here is based on the
knowledge of instantaneous velocity and radius values at only two sites. It
takes into account the presence of a reflection site of unknown reflection
coefficient, localised in the distal end of the vessel.
The values of wave speed and attenuation obtained with this method are in a
good agreement with the theory. This method has the advantage to be usable
for small portions of the arterial tree.
PACS: 47.15.-x – Laminar flows / 47.90.+a – Other topics in fluid dynamics
© EDP Sciences, 2007
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


