| Issue |
Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys.
Volume 31, Number 3, September 2005
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 217 - 223 | |
| Section | Physics of Biological Systems | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/epjap:2005062 | |
| Published online | 14 September 2005 | |
https://doi.org/10.1051/epjap:2005062
Statistical experimental design for studies of porosity and compressive strength in composite materials applied as biomaterials
Université de Rennes 1, Institut de Chimie, CNRS - UMR 6511,
Campus Beaulieu, 263 avenue du Général Leclerc,
35042 Rennes, France
Corresponding author: hassane.oudadesse@univ-rennes1.fr
Received:
2
November
2004
Revised:
3
March
2005
Accepted:
17
May
2005
Published online:
14
September
2005
Composites studied in this work are the associations of aluminosilicates and
13% of calcium phosphates. These composites present great interest. They
are destined to be applied in biomedical field, particularly in orthopedic
or jawbone surgery. Calcium phosphates are composed of HA (hydroxyapatite)
and TCP (tricalcic phosphate). The success of synthesised bony biomaterials
depends on two determinant factors: the porosity (which facilitate the cells
deposition and the vascularisation) and the compressive strength (which
permits the support of body charge). In this way, a statistical experimental
design was employed to quantify the influence of these two synthesis
parameters. It concerns the effect of the K2O/SiO2 molecular ratio
(X1) and the effect of the calcium phosphate (HA/TCP) weight %
(X2). The K2O/SiO2 molecular ratio characterises the
synthesis of the aluminosilicate. It varies between two limit levels: the
stoichiometric ratio K2O/SiO2 = 0.54 corresponding to:
 and the ratio K2O/SiO2 = 0.80 corresponding to
and the ratio K2O/SiO2 = 0.80 corresponding to 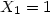 . In
bony biomaterials field, various calcium phosphates are commonly used as
biomaterials. In our previous works, the influence of the commercial
hydroxyapatite HA and tri-calcium phosphate TCP (13 wt%) addition was
investigated. To study the effect of calcium phosphate composition, the
weight percentage of mixing HA and TCP varied between two levels: the
composite aluminosilicate with 13 wt% of HA (
. In
bony biomaterials field, various calcium phosphates are commonly used as
biomaterials. In our previous works, the influence of the commercial
hydroxyapatite HA and tri-calcium phosphate TCP (13 wt%) addition was
investigated. To study the effect of calcium phosphate composition, the
weight percentage of mixing HA and TCP varied between two levels: the
composite aluminosilicate with 13 wt% of HA ( ) and the
composite aluminosilicate with 13 wt% of TCP (
) and the
composite aluminosilicate with 13 wt% of TCP (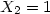 ). Eight samples
were studied. The statistical experimental design predicted answer surfaces
for compressive strength and percentage of porosity. After the validation of
models, it was possible to determine composite which presents best
compromise between percentage of porosity and compressive strength. This
composite will be evaluated by “in-vitro” and “in-vivo” studies to
investigate its potential for forthcoming applied as biomaterial.
). Eight samples
were studied. The statistical experimental design predicted answer surfaces
for compressive strength and percentage of porosity. After the validation of
models, it was possible to determine composite which presents best
compromise between percentage of porosity and compressive strength. This
composite will be evaluated by “in-vitro” and “in-vivo” studies to
investigate its potential for forthcoming applied as biomaterial.
PACS: 81.05.Mh – Cermets, ceramic and refractory composites / 68.55.Nq – Composition and phase identification / 72.80.Tm – Composite materials
© EDP Sciences, 2005
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


