| Issue |
Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys.
Volume 31, Number 1, July 2005
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 45 - 51 | |
| Section | Plasma, Discharges and Processes | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/epjap:2005039 | |
| Published online | 19 May 2005 | |
https://doi.org/10.1051/epjap:2005039
A comparative study of the behaviour of silver, copper and nickel submitted to a constant high power flux density
1
Laboratoire Arc Electrique et Plasmas Thermiques, CNRS UMR 6069,
Université Blaise Pascal, 63177 Aubière, France
2
Laboratoire de Mathématiques Appliquées, CNRS UMR 6620,
Université Blaise Pascal, 63177 Aubière, France
3
Laboratoire de Recherches sur la Réactivité des Solides, CNR UMR
5613, Université de Bourgogne, 21078 Dijon, France
Received:
23
November
2004
Revised:
10
January
2005
Accepted:
4
February
2005
Published online:
19
May
2005
In this paper, we present a numerical simulation of three metal cathode
(silver, copper and nickel) submitted to a constant flux power flux density
ranging between 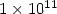 and
and 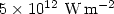 . The goal is
to compare the interface evolution (vaporization and liquefaction rate,
appearance time of liquid and vapour, energetic repartition) to predict the
behaviour of the cathodes during an electric arc.
. The goal is
to compare the interface evolution (vaporization and liquefaction rate,
appearance time of liquid and vapour, energetic repartition) to predict the
behaviour of the cathodes during an electric arc.
PACS: 52.80.Mg – Arcs; sparks; lightning; atmospheric electricity
© EDP Sciences, 2005
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


